Mercury Configuration
Mercury uses a toml configuration file. this documentation will go through each section to explain the configurable items of each section
Global Settings
Settings are defined in the [settings] block. options are:
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [settings] | manage_network_interfaces | "yes" | "yes"/"no" | allow mercury to add vip's to the network interfaces - required for internal proxy or for haproxy who does not add vip's. |
| [settings] | enable_proxy | "yes" | "yes"/"no" | use internal proxy for loadbalancing - not needed for external proxy programs, or dns only setup. |
Logging
Log settings are defined in the [logging] block. options are:
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [logging] | level | "info" | "(debug/info/warn/error)" | log level with debug being the most informative. |
| [logging] | output | "/var/log/mercury" | "(stdout/file)" | location to write the log information to Web Settings. |
Web
Web interface settings are defined in the [web] block. options are:
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [web] | binding | "0.0.0.0" | string | ip for the web interface to listen on |
| [web] | port | 9001 | int | port for the web interface to listen on |
| [web.tls] | tls | none | see TLS Attributes | TLS certificate information required for SSL |
| [web.auth.password] | username | none | sha256 password | username/password for admin rights in the gui (replace username with the username, and password with the sha256 of a password) |
| [web.auth.ldap] | host | none | "hostname/ip" | host of your ldap server |
| [web.auth.ldap] | port | 389 | int | port of your ldap server |
| [web.auth.ldap] | method | "tls" | "tls/ssl" | how to connect to your ldap server, ssl or tls |
| [web.auth.ldap] | binddn | none | string | the path to your CN (ex. "OU=Users,DC=example,DC=com"), we will apply the filter to this DN to find the user after authentication |
| [web.auth.ldap] | filter | none | string | filter to apply in binddn to find user (%s replaces the username used in login) (ex. "(&(objectClass=organizationalPerson)(uid=%s))") |
| [web.auth.ldap] | domain | none | string | the domain to prepend to the username during login |
| [web.auth.ldap.tls] | tls | none | see TLS Attributes | set insecureskipverify = true if required |
- note that when enabling LDAP, that local authentication no longer works and that an LDAP authenticated account is required.
Cluster
Cluster settings are defined in the [cluster] block. options are:
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [cluster.binding] | name | "" | string | Name of the cluster group |
| [cluster.binding] | addr | "" | string | ip to bind on for cluster communication |
| [cluster.binding] | authkey | "" | string | key required to connect to this cluster |
| [cluster.settings] | connection_timeout | 10 | int (seconds) | timeout connecting to remote cluster |
| [cluster.settings] | connection_retry_interval | 10 | int (seconds) | time in between retries connecting to the cluster |
| [cluster.settings] | ping_interval | 11 | int (seconds) | how often to send a ping to the remote host |
| [cluster.settings] | ping_timeout | 10 | int (seconds) | host long to wait for a ping timeout (generally 1 second less then interval) |
| [cluster.settings] | port | 9000 | int | port to listen on for cluster communication |
| [cluster.tls] | none | see TLS Attributes | TLS certificate information required for SSL | |
| [[cluster.nodes]] | array of loadbalancer nodes to connect to and form a cluster | |||
| [[cluster.nodes]] | name | string | name of a cluster node | |
| [[cluster.nodes]] | addr | string | address of a cluster node | |
| [[cluster.nodes]] | authkey | string | key used to connect to this cluster node |
DNS
DNS settings are defined in the [dns] block. options are:
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [dns] | binding | "0.0.0.0" | string | binding ip for dns service |
| [dns] | port | 53 | int | binding port for dns service |
| [dns] | allow_forwarding | [] | ["ip/mask"] | array of cidrs to allow dns forwarding requests |
| [dns] | allow_requests | [ "A", "AAAA", "NS", "MX", "SOA", "TXT", "CAA", "ANY", "CNAME", "MB", "MG", "MR", "WKS", "PTR", "HINFO", "MINFO", "SPF" ] | ["types"] | array of dns requests types we respond to |
TLS Attributes
TLS attributes are appended to any of the TLS keys in the config.
Usable in the settings for: cluster, web, listener, backend and Healthcheck
[cluster.tls]- for ssl settings on cluster communication[web.tls]- for ssl settings on the web gui[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.listener.tls]- for ssl settings on the pool listener[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.tls]- for ssl settings connecting to a backend node with ssl[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.healthcheck.tls]- for ssl settings for healthcheck connecting to a backend node with ssl
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [parent.tls] | minversion | "VersionTLS12" | string | Minimum TLS version required for this listener |
| [parent.tls] | maxversion | "" | string | Maximum TLS version required for this listener |
| [parent.tls] | ciphersuites | all | ["cipher"] | Cipher suites used by the listener (note that TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 is required for HTTP/2 support. see https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#pkg-constants for details |
| [parent.tls] | curvepreferences | all | ["curve"] | Curve preference used by the listener. see https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#pkg-constants for details. |
| [parent.tls] | certificatekey | "" | "/path/to/file" | file containing your ssl key |
| [parent.tls] | certificatefile | "" | "/path/to/file" | file containing your ssl certificate file |
| [parent.tls] | insecureskipverify | false | true/false | to to true to ignore insecure certificates, usable for self-signed certificates |
| [parent.tls] | clientauth | NoClientCert | string | server' policy for client authentication, see https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#ClientAuthType for details |
TLS Min/Max version
Supported versions are:
- VersionSSL30
- VersionTLS10
- VersionTLS11
- VersionTLS12
For details: https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#pkg-constants
TLS Ciphersuites
Supported ciphersuites are:
- TLS1.2
- TLS_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305
- TLS1.3
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- Fallback
- TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV
For details: https://golang.org/pkg/crypto/tls/#pkg-constants
TLS Recommended Cyphers and HTTP/2:
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 <- has to be first if you want HTTP/2 support!
The 4 cipers below are need for the best SSL-Labs certificate but do not support HTTP/2, the HTTP/2 one will slightly downgrade your score
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
These 3 ciphers are avilable for TLS1.3
- TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
TLS Curve preferences
Supported Curve preferences:
- CurveP256
- CurveP384
- CurveP521
- X25519
ACL Attributes
ACL attributes can adjust headers, cookies or allow/deny clients based on ip/headers
To adjust headers towards the client a rule should be applied on the outboundacl
To allow/deny clients based on headers/ip's a rule should be applied on the inboundacl
the ACL attribute should be an Array of acl's, you can add multiple.
Usable in the settings for: pools and backends
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.inboundacl]- applying an acl on all backends for a pool[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.inboundacl]- applying an acl on a specific backend only
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [[parent.inboundacl]] | inbound ACL's are applied on requests from loadbalancer to the backend - needs to be an array of ACL's executed top to bottom | |||
| [[parent.outboundacl]] | outbound ACL's are applied on requests from loadbalancer to the client - needs to be an array of ACL's executed top to bottom | |||
| ... | action | "" | see acl actions below | action to do when matching |
| ... | headerkey | "" | string | key of header (ex. "Content-Type") |
| ... | headervalue | "" | string | value of the header (ex. "UTF8") |
| ... | cookiekey | "" | string | key of the cookie |
| ... | cookievalue | "" | string | value of the cookie |
| ... | cookiepath | "" | string | path of the cookie |
| ... | cookieexpire | "" | datetime | expire date of the cookie |
| ... | cookiehttponly | bool | httponly cookie | |
| ... | cookiesecure | bool | secure cookie | |
| ... | conditiontype | "" | string | header/cookie status type to match with regex |
| ... | conditionmatch | "" | string | regex string to match |
| ... | urlmatch | "" | regex | match a request URL (e.g. /my/path/(.*)$ ) |
| ... | urlrewrite | "" | regex | rewrite a request URL (e.g. /new/path/$1) (does not work with the ACL special keys) |
| ... | statuscode | int | status code to return to the client (e.g. 500) | |
| ... | cidrs | ["ip/nm"] | cidr for use with allow/deny acl's (e.g. 127.0.0.1/32) | |
| ... | urlpath | "" | regex string | request path to which this acl applies. if path is set and does not match, acl is ignored. (e.g. ^/path/to/file ) |
ACL Actions
| Action | ACL Type | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Allow | Inbound | will deny a client if non of the allowed rules matches the client header/ip |
| Deny | Inbound | will deny a client if any of the deny rules matches the client header/ip |
| Rewrite | Inbound | will rewrite a url based on urlmatch and urlrewrite |
| Add | Inbound/Outbound | Adds a header/cookie given match. Only if it does not exist. |
| Replace | Inbound/Outbound | Replaces a header/cookie/status code given match. Only if it exists. |
| Remove | Inbound/Outbound | Removes a header/cookie given match Only if it exists |
| Modify | Inbound/Outbound | Modifies the supplied value of an existing entry (only works for Cookies) |
ACL special keys
The following special keys are translated in the ACL to a value. All values are placed between 3 hashes(#) on both sides. for example: ###NODE_ID###
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| NODE_ID | returns the uuid of the backend node |
| NODE_IP | returns the ip of the backend node |
| LB_IP | returns the ip of the listener |
| REQ_URL | returns the requested host + path |
| REQ_PATH | returns the requested path |
| REQ_QUERY | returns the encoded query values without the leading '?' |
| REQ_HOST | returns the requested host |
| REQ_IP | returns the ip of the requested host |
| CLIENT_IP | returns the remote addr of the client |
| UUID | returns a random UUID |
ACL Deny/allows
ACL's can be set to add/replace/modify headers, or to allow/deny requests based on headers/cidr (see examples above).
To use ALLOW/DENY, you must use the INBOUND acl. you cannot mix allow and deny ACL's together, this will result in only the allow beeing processed.
Examples
- deny all clients which user-agent specifies Macintosh
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.inboundacls]]
action = "deny"
header_key = "User-Agent"
header_value = ".*Macintosh.*"
- add a location header, effectively redirecting the user to the ssl if this came in on a http connection (see ACL Special keys)
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_REDIRECT.backends.redirect.outboundacls]]
action = "add"
header_key = "Location"
header_value = "https://###REQ_HOST######REQ_PATH###"
- allow only the local networks specified
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.inboundacls]]
action = "allow"
cidrs = ["10.10.0.197/32", "10.10.0.197/32"]
Stickyness Loadbalancing ACL
To use Stickyness you Must apply the following ACL. this will ensure that the correct cookie gets set to direct the client to its sticky backend node
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.outboundacls]]
action = "add"
cookie_expire = "24h"
cookie_httponly = false
cookie_key = "stky"
cookie_secure = true
cookie_value = "###NODE_ID###"
should the client be directed to another node that its initial sticky cookie, because its unavailable, we need to make sure that this new node is the sticky node for all future requests.
we do this by overwriting the node id with the ID of the new node.
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.outboundacls]]
action = "replace"
cookie_expire = "24h"
cookie_httponly = false
cookie_key = "stky"
cookie_secure = true
cookie_value = "###NODE_ID###"
adds a stky cookie with the node_id the client is connected to
SSL offloading adding/removing of Secure cookie add secure flag with responses to client we serve using https
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.outboundacls]]
action = "modify"
cookie_key = "ssloffloadedcookie"
cookie_secure = true
remove secure flag with responses to server listening on http
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.outboundacls]]
action = "modify"
cookie_key = "ssloffloadedcookie"
cookie_secure = false
rewrite all urls behind "/old/path" to "/new"
[[loadbalancer.pools.INTERNAL_VIP_LB.inboundacls]]
action = "rewrite"
urlmatch = "/old/path/(.*)$"
urlreplace = "/new/$1"
Rules Script
Rules can be applied in the form of scripts, the script can work with some basic testing
Scripts support the following functions:
| Function | Parameters | example | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| if | 3 | if $(variable) == "http" {...} | * value1 ("string" or number e.g. 12345) equator for strings: ==, !=, regex / for numbers: ==, <=, >=, != value2 ("string" or number to compare value 1 with) or regex "st[r]+.ng" value3 what to compare it with if a value needs to be parsed, enclose it like: $(value1) or $(value2) the statement if followed by curly brackets {...} to form the block which is executed if true |
| ifelse | 3 | elseif 1 == 1 {...} | see if |
| else | 0 | else { .. } | no parameter, the statement if followed by curly brackets {...} to form the block which is executed if true |
| var | 2 | var myvar = "hello" | create a new variable, followed by a value: param (name of parameter) value (can be "string" or number) |
| log | 1 | log "hello world" | log specified output to stdout - value to log ("string" or $(parameter)) |
| variable | 2 | variable = "https" | equator (=) new value ("string" or number or $(parameter)) |
| // # | infinite | # testing | comments, everything in comments is ignored |
| unset | 1 | unset response.header.server | removes a specific variable, or set it to empty |
note that when reading a variable you use $(variable.name) when you set a variable you use variable.name
Rule Types:
The following rule types exist:
- Pre-Inbound Rules - these are applied to the incoming connection from the client, before being processed by the proxy
- Inbound Rules - these are applied right before contacting the backend node of your pool, setting a response here will prevent the connection to the backend node
- Outbound Rules - these are applied after getting a reply from the backend node, before sending the response back to the client
This diagram describes when the specific rule script is applied 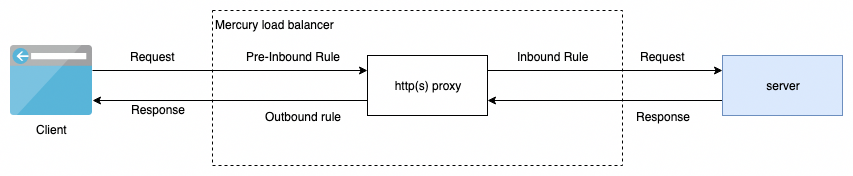
Modifiable attributes
You can change/read all fields as defined in the Golang
- request: [http.request][https://github.com/golang/go/blob/master/src/net/http/request.go#L108] type
- response: [http.response][https://github.com/golang/go/blob/master/src/net/http/response.go#L35] type
Rule Examples:
Pre-Inbound Rule: rewrite request to proxy:
the following is an example to rewrite some field in the request header
if $(request.host) == "example.com" {
// setting this only has effect on inbound rule
request.host = "another.host.com"
} ifelse $(request.host) == "domain.org" {
// note that request will be treated as if it was for another.host.com by the loadbalance mechanism
request.host = "another.host.com"
} else {
// do something
}
Inbound Rule: add api-key header to backend request for authentication on the backend server
request.header.x-api-key = "abcdefghijklmnop"
Inbound Rule: deny clients based on Client certificate verification
if $(request.tls.peercertificates.0.Signature) != "11:22:33:44:55:66:77:88" {
response.statuscode = 404
}
Inbound Rule: deny clients based on IP
if $(client.ip) match_net "10.10.10.0/24" {
response.statuscode = 404
}
Inbound Rule: Advanced Path rewrite before sending to backend
if $(request.url.path) match_regex "/user/(.*)" {
request.url.path replace_regex "/user/(.*)/" "/client/$1/"
}
Inbound Rule: Path rewrite with redirect
if $(request.url.path) match_regex "/user/(.*)" {
request.url.path = "/client/$1"
response.header.location = $(request.url)
response.statuscode = 301
}
Outbound Rule: Remove Server Header
unset response.header.server
ErrorPage Attributes
An error page is shown when an error is generated by Mercury, or if configured, when a 500 or higher error code is given by the backend application.
Usable in the settings for: pools and backends
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.errorpage]- applying an custom error page on all backends for a pool[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.errorpage]- applying an custom error page on a specific backend only
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [..errorpage] | file | "" | "/path/to/file" | Path to html file to serve if an error is generated |
| [..errorpage] | triggerthreshold | int | 500 | threshold to show error page, if the backend application reply is >= this value, it will show the error page. set this to 600 or higher if you do not want the loadbalancer to show an error page if the application generates a 500+ error message |
ErrorPage Handling
When a error page is set in the config, it will always show on internal errors (no backend available, or acl allow/deny) For errors given by a webserver you can use the trigger_threshold which will only trigger errors if the status code is equal or higher.
If you do not want the sorry page to show on return codes from the webserver, then set this to a higher number then the http error codes (e.g. 600 or up)
MaintenancePage Attributes
An maintenance page is shown when an healthcheck generates a "maintenance state" of if "maintenance" is set on a healthcheck via the gui As soon as there are no backends online, and one or more of the remaining node is in the state of "maintenance" this page will be shown. Any node in state maintenance will handle the existing requests, but no longer accept new requests.
Usable in the settings for: pools and backends
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.errorpage]- applying an custom error page on all backends for a pool[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.errorpage]- applying an custom error page on a specific backend only
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [..errorpage] | file | "" | "/path/to/file" | Path to html file to serve if an error is generated |
DNSEntry attributes
This specifies the dns entry for a backend, this will point to the loadbalancer serving the backend.
the dns entry will be balanced based across the loadbalancers based on the backend balance type.
Usable in the settings for: backends
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.dnsentry]- loadbalanced dns entry for this backend
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [..dnsentry] | hostname | "" | string | specifies the host entry for the dns record (e.g. "www") |
| [..dnsentry] | domain | "" | string | specifies the domain for the dns record (e.g. "example.com") |
| [..dnsentry] | ip | "" | string | specifies the IP for the record. If omitted the IP of the Pool listener is used. You should specify this if the IP is different then the IP where mercury is listening on |
Balance attributes
Loadbalancing is done based on the balance attributes. this applies to both global (dns) as internal (proxy) loadbalancing
Usable in the settings for: backends
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.balance]- load-balancing method used for this backend
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [..balance] | method | "" | "leastconnected" | This determains the type of load-balancing to apply (See Loadbalancing Methods below) |
| [..balance] | local_topology | [] | ["ip/nm"] | List of cidr's that defines the local network (e.g. [ "127.0.0.1/32" ]) |
| [..balance] | preference | int | value used for preference based load-balancing | |
| [..balance] | weight | int | value used for weighted based load-balancing | |
| [..balance] | active_passive | "no" | "yes"/"no" | set to yes if this will only be up on 1 of the clusters - only affects monitoring |
| [..balance] | clusternodes | calculated | int | (depricated) use serving_cluster_nodes instead |
| [..balance] | serving_cluster_nodes | calculated | int | the ammount of cluster nodes serving this backend - only affects monitoring (used for backend that are only available on 1 of multiple load-balancers) |
| [..balance] | serving_backend_nodes | calculated | int | the ammount of backend nodes serving this backend - only affects monitoring (used for when you expect x out of y nodes to be online always) |
Loadbalancing Methods
Loadbalancing Methods are applied in reverse order, meaning that the last entry is the first type of loadbalancing method beeing applied. the mechanism only orders the nodes, so the last method beeing applied (first entry) matters the most.
- a loadbalance method of
topology, leastconnectedwill first check the lease connected node, for all clients, and then check if any clients match the topology. forcing the clients that match the topology to this host. - a loadbalance method of
leastconnected,topologywill first check the client to see if it matches a topology, and then check the least connected node, ignoring previously applied topology based
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| leastconnected | balance based on current clients connected |
| leasttraffic | balance based on traffic generated |
| preference | balance based on preference set in node of backend (see preference attribute) |
| weighted | balance based on weight set in node of backend (see weight details below) |
| random | up to the rng gods |
| roundrobin | try to switch them a bit |
| sticky | balance based on sticky cookie. Important!: to apply sticky based loadbalancing you Must apply the Stickyness Loadbalancing ACL mentioned in the ACL Attribute section |
| topology | balance based on topology based networks. Note that this topology will match the server making the dns request, which is your DNS Server, not the client. Ensure that your cliens use the DNS server of their topology for this to work |
| responsetime | Loadbalance based on server response time, in theory a less busy server responds quicker, or if you have servers with difference service offerings. NOTE that this is a BETA Feature, and currently not suitable for production! |
| firstavailable | This limits the DNS records returned to 1. |
By default when balancing the available DNS records, all are returned. They are however ordered based on the loadbalancing methods above.
The following methods are an exception: sticky, topology and firstavailable. These methods will only return 1 record to ensure the client does not mistakenly connect to the second DNS record
Weighted loadbalancing
Weighted loadbalancing works by the weight set on the combined nodes.
For example if you have 2 nodes: - nodeA: 1 nodeB: 2 -> the sum is 3, so there is a 2/3rd chance of nodeB beeing selected - nodeA: 5 nodeB: 5 -> the sum is 10, so there is a 50% chance of either node beeing selected - nodeA: 9 nodeB: 1 -> the sum is 10, so there is a 90% chance of nodeA beeing selected
HealthCheck attributes
Health checks will be fired on backend nodes to ensure they can server requests. It is highly recommended to have a functional test here.
Usable in the settings for: pools and backends
[[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.healthchecks]]- health checks applicable to determain pool availability. if this failed all backends will fail.[[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backendname.healthchecks]]- health checks applicable to determain backend availability, only applies to the specific backend
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [[..healthchecks]] | type | "tcpconnect" | See HealthCheck | types for all available healthchecks to perform |
| [[..healthchecks]] | tcprequest | string | the data to send to a tcp socket for testing | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | tcpreply | string | the reply expected to a tcp socket for testing | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | httprequest | string | the request sent to a webserver (e.g. "http://www.example.com/") | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | httppostdata | string/special | post data sent to the host, see Specials Keys below for special parameters in the post string |
|
| [[..healthchecks]] | httpheaders | ["arrayofstrings"] | headers sent with the http request (e.g. [ 'Accept: application/json' ]) | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | httpstatus | 200 | int | http status code expected from backend |
| [[..healthchecks]] | httpreply | string/regex | string/regex expected in http reply from backend | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | httpfollowredirect | "yes" | string | makes the http healchecks follow redirects or not, note that this does not follow to different ports (e.g. 80 to 443) |
| [[..healthchecks]] | sshuser | "" | string | username to create a ssh session with |
| [[..healthchecks]] | sshpassword | "" | string | when set, use a password to authenticate |
| [[..healthchecks]] | sshkey | "" | string | ssh private key joined with line breaks (e.g. "-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEpAIBAA...FA==\n-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----") |
| [[..healthchecks]] | pingpackets | 4 | int | number of ping packets to send (only when 100% packetloss this will be reported as down) |
| [[..healthchecks]] | pingtimeout | 1 | int (seconds) | timeout in seconds for each ping request |
| [[..healthchecks]] | ip | node.IP | alternative IP to send request to | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | port | node.Port | alternative Port to send request to | |
| [[..healthchecks]] | sourceip | listener.IP | string | alternative source IP to use when sending request |
| [[..healthchecks]] | interval | 10 | int | how often to check this backend |
| [[..healthchecks]] | timeout | 10 | int (seconds) | how long to wait for backend to finish its reply before reporting it in error state |
| [[..healthchecks]] | online_state | "online" | online/offline/maintenance | if the healtcheck sais its online, instead send this alternative state |
| [[..healthchecks]] | offline_state | "offline" | online/offline/maintenance | if the healtcheck sais its offline, instead send this alternative state |
| [[..healthchecks.tls]] | [web.tls] | tls | none | see TLS Attributes |
HealthCheck types
The following types are available: Type | Description --- | --- tcpconnect | does a simple tcp connect tcpdata | connect to the host. sends tcprequest and expects tcpreply string to match the answer httpget | performs a GET request on the backend using the http* attributes. If httpreply is not provided only the httpstatus will be matched httppost | same as httpget, only performs a POST instead of a GET icmpping | does a icmpping for the amount of pingpackets and will report down if there is 100% packetloss tcpping | does a tcpping for the amount of pingpackets and will report down if there is 100% packetloss udpping | does a udpping for the amount of pingpackets and will report down if there is 100% packetloss ssh | does ssh authentication at the remote host
Special Keys
The following special keys are translated in the httppostdata to a value
All values are placed between 3 hashes(#) on both sides. for example: ###DATE### Key | Description --- | --- DATE | returns todays date in system timezone DATEUTC | returns todays date in UTC timezone DATE+(number)[s|m|h]FORMAT | returns todays date + number (seconds/minutes/hours) in FORMAT - see https://golang.org/pkg/time/ for FORMAT options DATE-(number)[s|m|h]FORMATUTC | returns todays date - number (seconds/minutes/hours) in UTC
example: httppostdata= "<date>###DATE+5m2006-01-02T15:04:05.000Z|UTC###</date>" will post this xml date with the value of todays date in the format 2006-01-02T15:04:05.000Z in UTC time and add +5 minutes.
Creating a Loadbalance Pool
A Loadbalance pool consists of a attributes defining a pool, and should contain a backend pool to work
Adding a Pool
A Pool defines a group of backends. a pool needs a listener when in proxy mode, but when only using dns based loadbalancing this can be omitted
Usable in the settings for: loadbalancer.pools where a pool is named using a uniq poolname
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname]- poolname must be a uniq name to identify the pools
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [..listener'] | describes to where the pool should listen on, and how it should handle requests | |||
| [..listener'] | ip | string | IP address where the Pool should listen on when using the internal loadbalancer | |
| [..listener'] | port | 80 | int | Port the pool should listen on for requests |
| [..listener'] | mode | "http" | http/https/tcp | The protocol this listener should support. Available: "http", "https", "tcp" |
| [..listener] | httpproto | 2 | int | Set to 1 to enforce HTTP/1.1 instead of HTTP/2 http requests (required for websockets) |
| [..listener.tls] | tls | none | see TLS Attributes | TLS settings for use with this listener (required for https) |
| [[..inboundacl]] | array of acls | see ACL Attributes | Inbound ACLs are applied on incomming traffic from a client, before beeing sent to a backend server. ACLs on the listener are applied to all backends | |
| [[..outboundacl]] | array of acls | see ACL Attributes | Outbound ACLs are applied on outgoing traffic from a webserver, before beeing sent to the customer. ACLs on the listener are applied to all backends | |
| [[..inboundrule]] | array of (multiline) strings | see Rules Script | Inbound Rules is a script of whiles which are applied on incomming traffic from a client, before beeing sent to a backend server. Rules on the listener are applied to all backends | |
| [[..outboundrule]] | array of (multiline) strings | see Rules Script | Outbound Rules is a script of whiles which are applied on outgoing traffic from a webserver, before beeing sent to the customer. Rules on the listener are applied to all backends | |
| [[..errorpage]] | see ErrorPage Attributes | Specifies a custom error page, to show if errors do occur. When adding an error page to a pool, it applies to all backends | ||
| [[..backends]] | see Backend Attributes | Specifies the backends for a pool | ||
| [[..healthchecks]] | see Healthcheck Attributes | a healtcheck put on a pool, will affect ALL backends of this vip (e.g. usefull for testing your internet connectivity) |
Adding a Backend
A Pool can have multiple Backend only if the listening mode of the pool is http or https. for tcp there can be only 1 backend.
Usable in the settings for: backends where a backend is named using a uniq backendname
[loadbalancer.pools.poolname.backends.backenname]- backend name must be a string that defines the name of the backend
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [[.backendname.inboundacl]] | array of acls | see ACL Attributes | Inbound ACLs are applied on incomming traffic from a client, before beeing sent to a backend server. | |
| [[.backendname.outboundacl]] | array of acls | see ACL Attributes | Outbound ACLs are applied on outgoing traffic from a webserver, before beeing sent to the customer. | |
| [.backendname.errorpage] | see ErrorPage Attributes | Specifies a custom error page, to show if errors do occur. | ||
| [.backendname.dnsentry] | see BackendDNS Attributes | Specifies which DNS entry to balance across this backend. The DNS entry will point to the loadbalance that can serve requests to this backend | ||
| [..backendname.balance] | see Balance attributes | Balance defines the balance modes for this backend. | ||
| [[.backendname.healthchecks]] | array of healthchecks | see Healthchecks Attributes | Healthchecks specifie what to check in order to determain if the backend is serving requests. | |
| [..backendname] | healthcheckmode | "all" | all/any | Specifies wether all or only 1 check should succeed before the backend is marked as down |
| [..backendname] | hostnames | ["arrayofstrings"] | List of hostnames this backend serves. the client is redirected to this backend base on the client request header. This applies to http(s) only | |
| [..backendname] | connectmode | "http" | string | how do we connect to the backend see Connection Methods below |
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | array of nodes that are part of this backend | |||
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | ip | string | IP of backend node | |
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | port | int | port of backend node | |
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | name | string | name of backend node | |
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | preference | int | preference of node for preference based loadbalancing | |
| [[..backendname.nodes]] | local_topology | string | local topology group name of node for preference based loadbalancing |
Connection Methods
The following connection methods are available for connecting to a backend: Type | Description --- | --- http | for serving http requests to the backend node https | for serving https requests to the backend node tcp | for serving tcp requests to the backend node internal | for not sending a request to a backend but handle this internaly (see example on Http to Https redirect)
Adding Static DNS Records
You can add static DNS entries to Mercury. You might want this if you want to loadbalance a your TLD domain. (example.org) instead balancing sub domains (www.example.org)
Note that if your using Mercury as DNS server, that we do not yet support DNSSEC
the records contains a array of hashes with dns records
Usable in the settings for: dns
[[dns.domains.domainname.records]]- domainname must be the domain of which the records apply to
| Key | Option | Default | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [[..records]] | name | string | host name of the dns record for the domain (e.g. "www") | |
| [[..records]] | type | string | type of dns record (e.g. "A") | |
| [[..records]] | target | string | target of the record (e.g. "1.2.3.4") |
Static DNS Records examples:
Below are some examples of common DNS records: example A record for dns1 (in the previously defined domain)
[[dns.domains."glb.example.com".records]]
name = "dns1"
type = "A"
target = "1.2.3.4"
example ipv6 record pointing dns1 to a ipv6 ip
[[dns.domains."glb.example.com".records]]
name = "dns1"
type = "AAAA"
target = "::1"
example NS record for the domain to point to dns1.example.com
[[dns.domains."glb.example.com".records]]
name = ""
type = "NS"
target = "dns1.example.com"
example SOA record for the domain
[[dns.domains."glb.example.com".records]]
name = ""
type = "SOA"
target = "dns1.example.com. hostmaster.example.com. ###SERIAL### 3600 10 10"
example MX record for the domain to mx1.example.com with a preference of 20
[[dns.domains."glb.example.com".records]]
name = ""
type = "MX"
target = "20 mx1.example.com."